How to operate a drone? It’s a question sparking increasing curiosity as these versatile machines become more accessible. From navigating complex flight paths to capturing breathtaking aerial footage, operating a drone offers a unique blend of technological mastery and artistic expression. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to confidently take to the skies, covering everything from pre-flight checks and safety procedures to advanced maneuvers and legal considerations.
Whether you’re a novice pilot or looking to refine your skills, prepare for a comprehensive exploration of the world of drone operation.
We’ll delve into the nuances of different drone types, exploring their unique operational characteristics and control interfaces. Mastering the art of smooth takeoffs, landings, and precise navigation will be covered step-by-step, along with crucial safety protocols to ensure responsible and legal operation. Finally, we’ll unlock the creative potential of drone photography and videography, enabling you to capture stunning aerial perspectives.
Drone Types and Their Operation

Understanding the different types of drones and their operational characteristics is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will explore the key distinctions between multirotor, fixed-wing, and single-rotor drones, focusing on their control interfaces, specific models, and performance capabilities.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, from basic controls to advanced maneuvers, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and enhance your piloting skills. Safe and responsible drone operation is paramount for both personal safety and legal compliance.
Multirotor, Fixed-Wing, and Single-Rotor Drone Differences
Multirotor drones, commonly known as quadcopters (four rotors) or hexacopters (six rotors), offer exceptional maneuverability and stability due to their multiple rotors. They are ideal for aerial photography, videography, and inspections in confined spaces. Fixed-wing drones, resembling airplanes, are generally faster and have longer flight times but require runways for takeoff and landing, limiting their use to open areas.
Single-rotor drones, or helicopters, offer vertical takeoff and landing capabilities similar to multirotors, but are less common due to their complexity and higher maintenance requirements. Operational differences primarily lie in their control schemes and flight characteristics; multirotors are controlled via six-axis input (three for position, three for attitude), while fixed-wing drones often require more nuanced control over throttle, ailerons, elevator, and rudder.
Drone Control Interfaces
Control interfaces vary significantly across drone models. Many utilize standard radio controllers with joysticks for maneuvering and buttons for camera control, flight modes, and return-to-home functions. Some advanced models integrate GPS and obstacle avoidance systems, simplifying operation. Smartphone apps provide alternative control options, often with intuitive interfaces and real-time telemetry data. Examples include DJI’s smart controllers and apps, which offer advanced features and streamlined control for their drone models.
Specific Drone Models and Operational Characteristics
DJI Mavic 3 boasts impressive camera capabilities and obstacle avoidance, while the Autel Evo II offers long flight times and high-resolution video recording. Fixed-wing drones like the Parrot Anafi USA provide extended range but require more skilled piloting. The operational characteristics of each model are determined by factors like motor power, battery capacity, and software features. For example, some drones are designed for high-speed maneuvers, while others prioritize stability and precision.
Drone Type Comparison
| Drone Type | Flight Time (minutes) | Payload Capacity (kg) | Range (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multirotor (DJI Mavic 3) | 46 | 0.5 | 15 |
| Fixed-Wing (Parrot Anafi USA) | 45 | 0.25 | 40 |
| Single-Rotor (rare example needed – data speculative) | 30 | 1 | 10 |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is paramount for safe drone operation. This section Artikels essential checks, emergency procedures, and safety regulations to ensure responsible and accident-free flights.
Pre-Flight Checklist

Before each flight, meticulously inspect your drone and its components. This includes verifying battery levels (fully charged and properly connected), inspecting propellers for damage or imbalance, and ensuring a strong GPS signal. Confirm that all control linkages are secure and that the drone’s camera and gimbal are functioning correctly. Check the weather conditions to ensure they are suitable for safe flight, avoiding strong winds or precipitation.
Emergency Procedures
Loss of signal and low battery are common emergencies. If signal is lost, most drones have a “return-to-home” (RTH) function that will automatically guide the drone back to its starting point. In low-battery situations, immediately initiate the RTH function or attempt a controlled landing. Always have a backup plan in place and be prepared to take manual control if needed.
Understanding your drone’s capabilities and limitations is essential for effective emergency response.
Safe Pre-Flight Inspection Flowchart
A visual flowchart, while not directly represented in HTML, would depict a sequential process: Battery check -> Propeller inspection -> GPS signal verification -> Camera/Gimbal check -> Control linkage check -> Weather check -> Flight authorization.
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Never fly near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Respect privacy and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Adhere to all local and national drone regulations.
- Fly responsibly and avoid endangering people or property.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Mastering drone controls is essential for safe and effective flight. This section details the function of control elements, provides a step-by-step guide for basic maneuvers, and offers tips for navigating various environments.
Drone Remote Control Functions
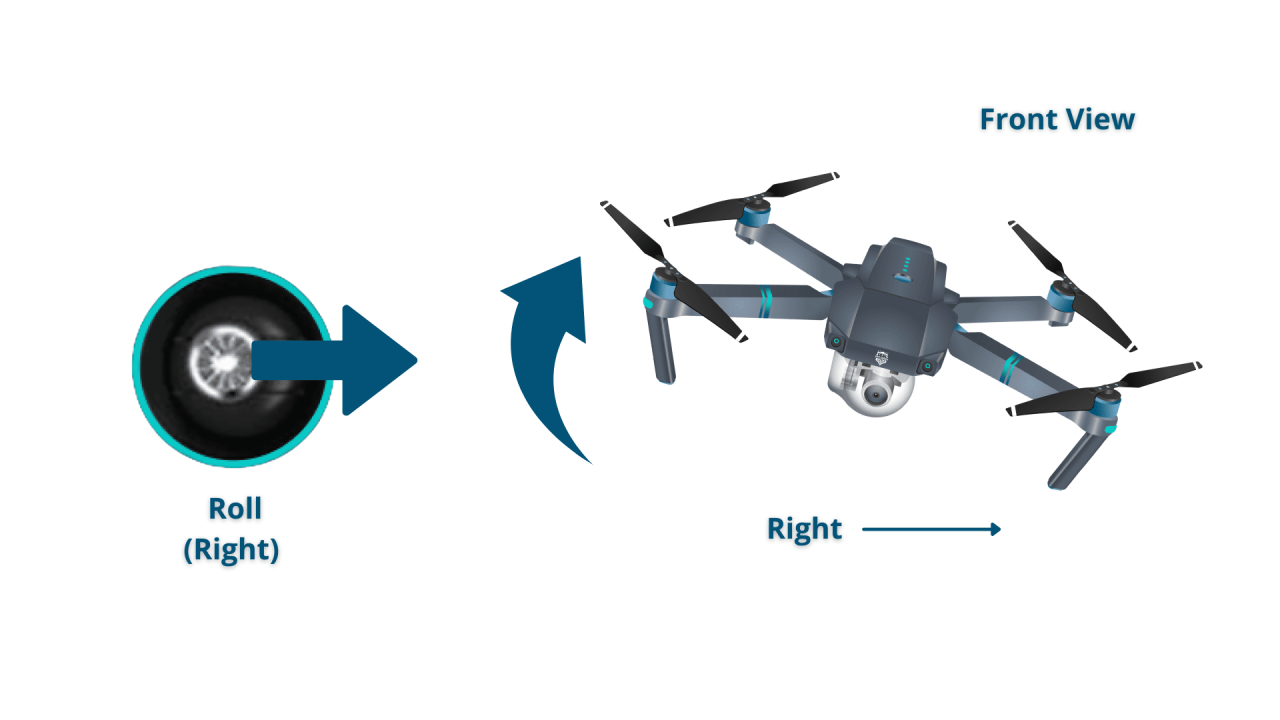
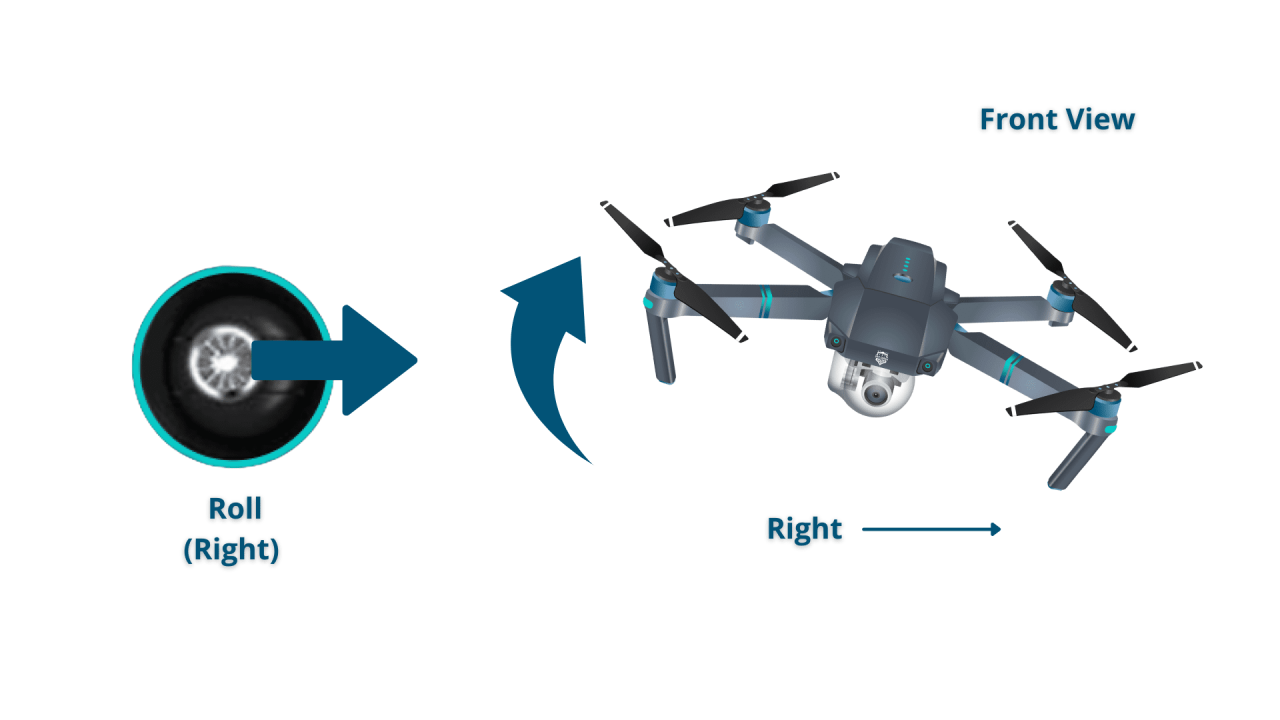
A typical drone remote has two joysticks: one controls the drone’s yaw (rotation) and altitude (vertical movement), the other controls its roll (tilt left/right) and pitch (tilt forward/backward). Buttons on the remote typically control functions such as camera operation, flight mode selection, return-to-home, and emergency stops. Understanding the mapping of these controls is crucial for precise drone maneuvers.
Taking Off, Hovering, and Landing
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Calibrate the compass and GPS (if necessary).
- Wait for the GPS signal to lock.
- Slowly raise the drone using the throttle stick.
- Use the other joystick to maintain a stable hover.
- To land, slowly lower the drone using the throttle stick.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Navigation in Various Environments
Navigating in windy conditions requires careful control and adjustment of the throttle to maintain stability. Flying in confined spaces necessitates precise maneuvering and awareness of obstacles. Understanding the drone’s capabilities and limitations is crucial for safe and successful navigation in different environments.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of safety regulations and technical proficiency. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and become a confident pilot. Safe and responsible drone operation is paramount for both personal safety and legal compliance.
Compass and GPS Calibration
Calibrating the compass involves rotating the drone horizontally in a figure-eight pattern, allowing the internal compass to accurately orient itself. GPS calibration often involves holding the drone stationary for a period to allow it to acquire a strong satellite signal, ensuring accurate positioning.
Advanced Drone Maneuvers and Techniques: How To Operate A Drone
This section explores advanced techniques to enhance drone control and flight capabilities, including smooth camera movements and more complex maneuvers.
Smooth and Precise Movements
Achieving smooth camera panning and tilting requires precise control of the gimbal’s movement. Practicing slow, deliberate movements will result in smoother footage. Techniques like using the drone’s follow-me mode or waypoint navigation can further enhance the stability and precision of camera movements.
Advanced Maneuvers (If Applicable)
Many multirotor drones offer advanced maneuvers like flips and rolls, but these should only be attempted in safe, open spaces with a high level of piloting skill. These maneuvers require a good understanding of the drone’s responsiveness and control inputs to avoid accidents.
Planning and Executing Complex Flight Paths
Advanced drones often have waypoint navigation systems that allow users to plan and execute complex flight paths. This involves setting a series of waypoints on a map, and the drone will autonomously navigate between these points. Careful planning is essential to avoid obstacles and ensure safe flight.
Stable Hover in Challenging Conditions
- Maintain constant throttle input.
- Use small, precise joystick movements.
- Adjust for wind gusts by countering their effect.
- Utilize advanced flight modes if available.
- Practice regularly to improve stability.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and safe operation of your drone. This section details maintenance procedures and troubleshooting common malfunctions.
Regular Drone Maintenance
Regularly clean the drone’s body, propellers, and camera lens to remove dirt and debris. Inspect all components for signs of damage or wear. Pay particular attention to the motor mounts, propellers, and battery connections. Store the drone in a dry, clean environment to prevent corrosion and damage.
Replacing Propellers and Batteries
Replacing drone propellers involves carefully removing the damaged propeller and securely attaching a new one. Ensure the propellers are correctly aligned and tightened. Battery replacement involves carefully disconnecting the old battery and securely connecting the new one, ensuring proper polarity.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Solutions
Common malfunctions include motor failures (check motor connections and replace if needed), GPS signal loss (check for obstructions and ensure proper calibration), and low battery warnings (replace or recharge the battery). Consult your drone’s manual for specific troubleshooting instructions.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
| Component | Maintenance Task | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspection for damage | Before each flight |
| Battery | Check voltage and charge | Before each flight |
| Motors | Visual inspection | Monthly |
| Body | Cleaning | After each flight |
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to all relevant laws and regulations. This section highlights key legal aspects of drone operation.
Relevant Laws and Regulations
Drone regulations vary by location and are constantly evolving. It is crucial to research and understand the specific laws and regulations in your area before operating a drone. These regulations often cover areas such as registration requirements, airspace restrictions, and operational limitations.
Drone Registration and Permits
Many jurisdictions require drone registration before operation. The registration process typically involves providing information about the drone and its owner. Some activities, such as commercial drone operations, may require additional permits and licenses.
Airspace Restrictions and Limitations
Airspace restrictions typically prohibit drone flights near airports, military bases, and other sensitive areas. Height restrictions may also be in place to prevent collisions with manned aircraft. Understanding these limitations is crucial for safe and legal drone operation.
Best Practices for Responsible and Legal Drone Operation
- Register your drone according to local regulations.
- Check airspace restrictions before each flight.
- Maintain visual line of sight.
- Respect privacy and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Fly responsibly and avoid endangering people or property.
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning photos and videos. This section explores techniques for achieving high-quality aerial footage.
Setting Up and Using a Drone Camera
Setting up the drone camera involves adjusting settings such as resolution, frame rate, and ISO. Familiarize yourself with the camera’s controls and features. Practice using different shooting modes and settings to achieve the desired results. Ensure the camera is properly balanced and secured to the gimbal.
Tips and Techniques for Capturing Stunning Aerial Footage, How to operate a drone
Plan your shots carefully, considering composition, lighting, and the overall narrative. Use smooth, deliberate movements to avoid shaky footage. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to capture unique shots. Consider using filters or post-processing techniques to enhance the final product.
Importance of Proper Lighting and Composition
Proper lighting is crucial for achieving high-quality images. Avoid shooting in harsh sunlight, which can create harsh shadows. Consider using a polarizing filter to reduce glare and enhance color saturation. Composition involves arranging elements within the frame to create a visually appealing image. Use the rule of thirds and other compositional guidelines to create balanced and dynamic shots.
Examples of Creative Aerial Shots
Examples include establishing shots showcasing the vastness of a landscape, dynamic shots following a moving subject, and close-up shots revealing intricate details. The use of different camera angles, such as low-angle shots or high-angle shots, can significantly enhance the visual impact of the footage.
Successfully operating a drone is a rewarding experience, blending technological skill with creative vision. By diligently following pre-flight checklists, understanding your drone’s controls, and adhering to safety regulations, you can unlock a world of possibilities. Remember, continuous practice and a commitment to responsible operation are key to becoming a proficient and safe drone pilot. This guide has provided a foundation; now it’s time to take flight and explore the skies responsibly.
FAQ Explained
What is the best drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring features like GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home functions. Research models known for ease of use and positive user reviews.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies significantly depending on the model and flight conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for an estimated flight time, but expect shorter flight times in windy conditions or with heavier payloads.
What happens if I lose signal with my drone?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that automatically brings the drone back to its takeoff point if signal is lost. However, always fly within visual line of sight to mitigate risks.
Do I need insurance for my drone?
Drone insurance is recommended, especially for commercial use. Check your local regulations to determine whether insurance is mandatory and the level of coverage required.